Let us first understand what software engineering stands for. The term is made of two words, software and engineering.
Software is more than just a program code. A program is an executable code, which serves some computational purpose. Software is considered to be collection of executable programming code, associated libraries and documentations. Software, when made for a specific requirement is called software product.
Engineering on the other hand, is all about developing products, using well-defined, scientific principles and methods.
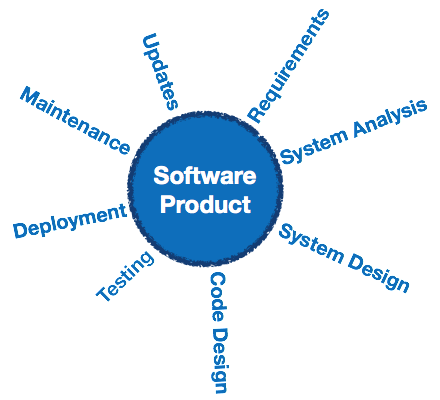
Software engineering is an engineering branch associated with development of software product using well-defined scientific principles, methods and procedures. The outcome of software engineering is an efficient and reliable software product.
IEEE defines software engineering as:
The application of a systematic,disciplined,quantifiable approach to the development,operation and maintenance of software; that is, the application of engineering to software.
The study of approaches as in the above statement.
Fritz Bauer, a German computer scientist, defines software engineering as:
Software engineering is the establishment and use of sound engineering principles in order to obtain economically software that is reliable and work efficiently on real machines.
The process of developing a software product using software engineering principles and methods is referred to as software evolution. This includes the initial development of software and its maintenance and updates, till desired software product is developed, which satisfies the expected requirements.
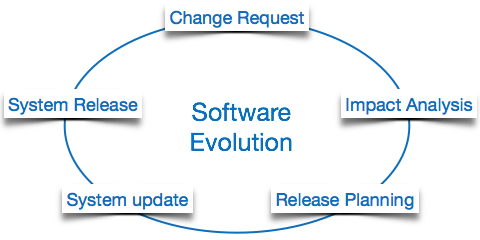
Evolution starts from the requirement gathering process. After which developers create a prototype of the intended software and show it to the users to get their feedback at the early stage of software product development. The users suggest changes, on which several consecutive updates and maintenance keep on changing too. This process changes to the original software, till the desired software is accomplished.
Even after the user has desired software in hand, the advancing technology and the changing requirements force the software product to change accordingly. Re-creating software from scratch and to go one-on-one with requirement is not feasible. The only feasible and economical solution is to update the existing software so that it matches the latest requirements.
Lehman has given laws for software evolution. He divided the software into three different categories:
Lehman has given eight laws for E-Type software evolution -
Software paradigms refer to the methods and steps, which are taken while designing the software. There are many methods proposed and are in work today, but we need to see where in the software engineering these paradigms stand. These can be combined into various categories, though each of them is contained in one another:
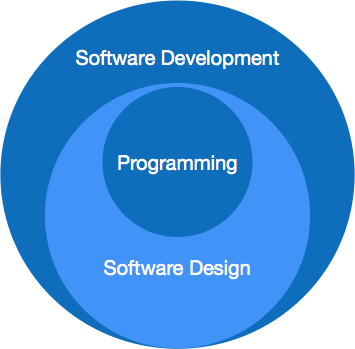
Programming paradigm is a subset of Software design paradigm which is further a subset of Software development paradigm.
This Paradigm is known as software engineering paradigms where all the engineering concepts pertaining to the development of software are applied. It includes various researches and requirement gathering which helps the software product to build. It consists of –
This paradigm is a part of Software Development and includes –
This paradigm is related closely to programming aspect of software development. This includes –
The need of software engineering arises because of higher rate of change in user requirements and environment on which the software is working.
A software product can be judged by what it offers and how well it can be used. This software must satisfy on the following grounds:
Well-engineered and crafted software is expected to have the following characteristics:
This tells us how well software works in operations. It can be measured on:
This aspect is important when the software is moved from one platform to another:
This aspect briefs about how well a software has the capabilities to maintain itself in the ever-changing environment:
In short, Software engineering is a branch of computer science, which uses well-defined engineering concepts required to produce efficient, durable, scalable, in-budget and on-time software products.