|
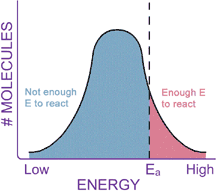
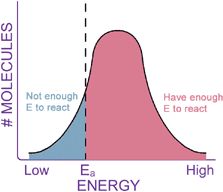
CONCLUSIONKinetics is the study of chemical reaction rates. Different reactions proceed at different rates. Some chemicals react with each other very quickly, while others react very slowly. Kinetics should not be confused with thermodynamics, which tells how likely the reaction is. Collision theory tells us that reaction rates are determined by how often the reactant molecules bump into each other (related to concentration), and how fast they are moving when they collide (related to temperature). Reaction rates can be greatly increased by the addition of a catalyst, which lowers the energy barrier, or activation energy, of a reaction.
For elementary or simple single-step processes, the balanced chemical reaction can be used to construct a rate equation for the reaction. The rate equation correlates the speed of a reaction with the concentrations of reactants, through the rate constant, k.
However, the rate constant for a nonelementary reaction must be determined through experimentation. It is impossible to tell just by looking at a written chemical reaction whether it is an elementary process, or whether the reaction actually goes through several intermediates to form the products. The equilibrium constant, Keq, which is the ratio of products to reactants when the reaction has gone to completion, is determined by the tug-of-war between the forward and reverse reaction rates of the chemical reaction:
Remember, catalysts are not consumed in the reaction they catalyze, and they don’t change the Keq of a reaction, nor do they change the DG of the reaction. Catalysts increase reaction rates by helping reactants get through the transition state, in effect lowering the activation energy (DG‡, or Ea) of a reaction. You have completed this exercise.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||